In the posting process, transactions from the journal are organized and categorized into their respective ledger accounts. The general ledger accounts utilize double-entry bookkeeping, which is an essential principle in accounting. Double-entry bookkeeping states that for every transaction, there must be a debit entry and a credit entry.
What is a Chart of Accounts? A How-To with Examples
However, it lists only permanent accounts because all temporary accounts get closed in step 8 above. The post-closing trial balance serves as the base or opening trial balance for the next period’s accounting cycle. After the adjusting entries have been passed and posted to respective ledger accounts, the unadjusted trial balance needs to be corrected to show the impact of these adjustments. For this purpose, an amended trial balance, known as an adjusted trial balance, is prepared.
General Journal

Book a demo today to see what running your business is like with Bench. We recommend reading our article on this subject so that you can choose the approach that makes the most sense for your business.
Balance Sheet and Cash Flows
The accounting cycle is a methodical set of rules that can help ensure the accuracy and conformity of financial statements. Computerized accounting systems and the uniform process of the accounting cycle have helped to reduce mathematical errors. Is keeping up with the accounting cycle taking up too much of your time? With Bench, you get access to your own expert bookkeeper to collaborate with as you grow your business.
What is the simple example of the accounting period concept?
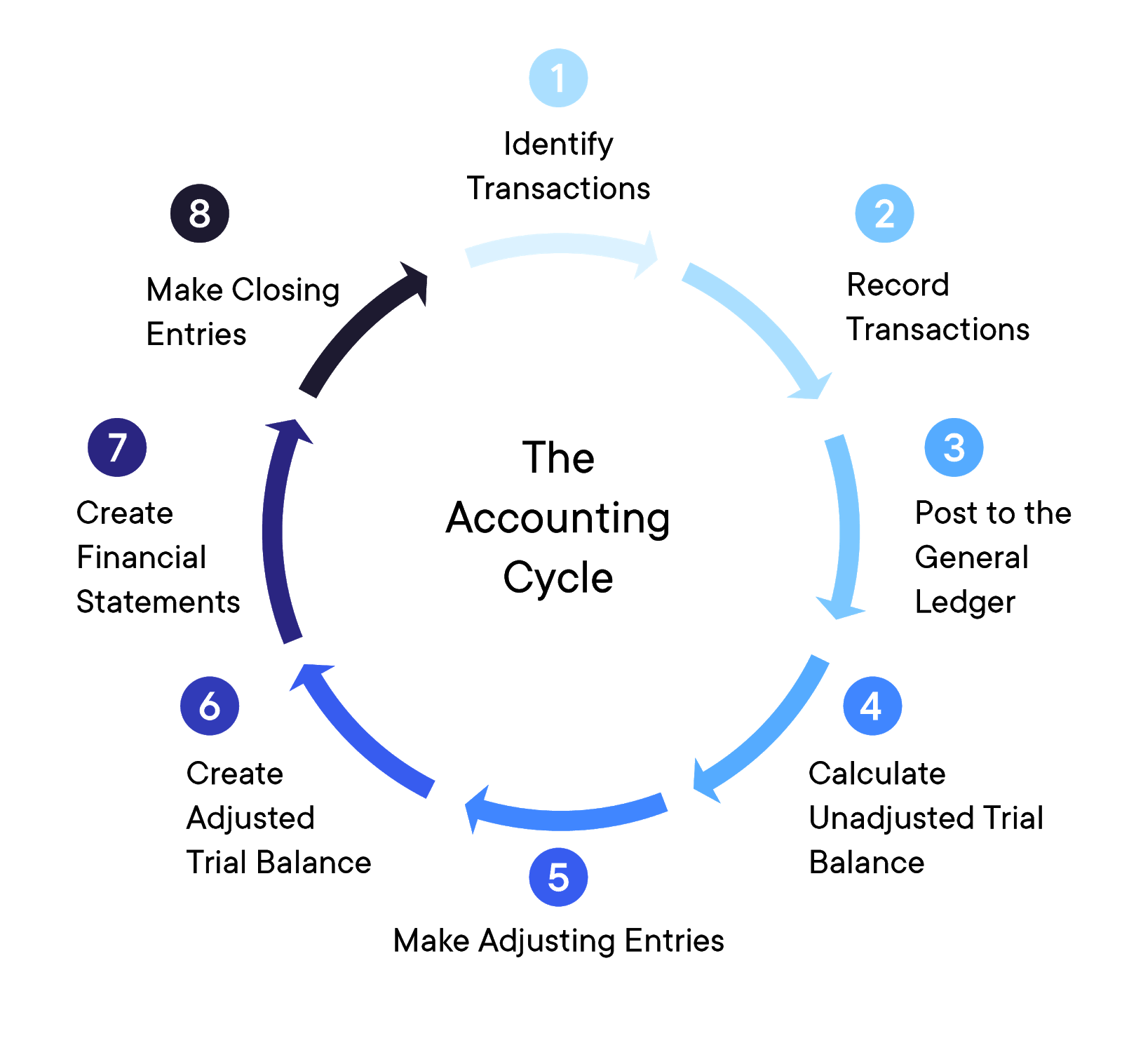
The main difference between the accounting cycle and the budget cycle is that the accounting cycle compiles and evaluates transactions after they have occurred. The budget cycle is an estimation of revenue and expenses over a specified period of time in the future and has not yet occurred. A budget cycle can use past accounting statements to help forecast revenues and expenses. Analyzing a worksheet and identifying adjusting entries make up the fifth step in the cycle. A worksheet is created and used to ensure that debits and credits are equal. The eight-step accounting cycle starts with recording every company transaction individually and ends with a comprehensive report of the company’s activities for the designated cycle timeframe.
- But if you use accounting software, you won’t need to prepare the trial balance manually.
- If a transaction is identified but it isn’t recorded, then it’s like it never happened at all.
- Once you check off all the steps, you can move to the next accounting period.
There are many essential parts of your business’s operations and keeping accurate financial records is fundamental among them. Let accounting software work behind the scenes to perform critical tasks. You can then use your time and resources to make strategic decisions with the information you’ve gathered from these key reports.
This article delves into the nuances of these steps and highlights its significance in promoting transparency, accountability, and well-informed decision-making in the business sphere. Additionally, we explore the impact of technology as a catalyst in optimizing the efficiency and effectiveness of the accounting cycle, streamlining routine tasks and augmenting accuracy. The general ledger (GL) is a master record of all transactions categorized into specific categories such as cost of goods sold (COGS), accounts payable, accounts receivable, cash, and more. An optional step at the beginning of the next accounting period is to record and post reversing entries. In this step, the adjusting entries made for accrual of income, accrual of expenses, deferrals under the income method, and prepayments under the expense method are reversed.
When the accounting period ends, you’ll adjust journal entries to fix any mistakes and anomalies found during the worksheet analysis. Since this is the final step before creating financial statements, you should double-check everything with the help of a new adjusted trial balance. The main purpose of drafting an unadjusted trial balance is to check the mathematical accuracy of debit and credit entries recorded under previous steps. Obviously, business transactions occur and numerous journal entries are recording during one period. The accounting cycle plays a crucial role in financial reporting by providing a structured and systematic process for recording, organizing, and presenting a company’s financial information.
This is a straightforward guide to the chart of accounts—what it is, how to use it, and why it’s so important for your company’s bookkeeping. In other words, deferrals remove transactions that do not belong to the period you’re creating a financial statement stp and finalisation for. Once you’ve made the necessary correcting entries, it’s time to make adjusting entries. Recording entails noting the date, amount, and location of every transaction. Next, you’ll break down (or analyze) the purpose of each transaction.
Accounting concepts are fundamental principles that guide the accounting cycle. Some key concepts are the accrual basis of accounting, the matching principle, and the revenue recognition principle. These concepts shape how transactions are identified, recorded, adjusted, and reported in financial statements to ensure that financial information is relevant, reliable, and comparable. The process of closing temporary accounts includes recording closing entries.

